Whole Body Hyperthermia
The beneficial effects of fever on the body have been known since ancient times. In the 5th century BC, Parmenides stated, "Give me the power to produce fever, and I will cure any disease." Additionally, Hippocrates and Galen artificially induced fever to treat certain conditions, especially psychological ones.
Fever is a natural defense mechanism of the human body. The immune system's defense cells function most effectively at temperatures above 39ºC.
Clinical experience has shown that at this elevated temperature, all metabolic and detoxification processes are intensely stimulated, which helps in overcoming infections, inflammation, and pain more quickly and efficiently.
During a fever, the accumulation of sweat activates the excretion of toxic substances, purifying the body and improving metabolism. After the fever, the body relaxes, and the pain disappears.
Applications of whole-body
hyperthermia include
- cancer therapy (as part of a comprehensive immune system stimulation program).
- immunotherapy (boosting the body's defenses during various types of chronic infections, including bronchial asthma).
- pain therapy (for chronic and systemic pain, especially when other pain management methods have failed).
- rheumatism therapy (soft tissue rheumatism, fibromyalgia, ankylosing spondylitis, scleroderma, advanced stages of rheumatoid arthritis).
- skin conditions (psoriasis, neurodermatitis, allergic skin conditions).
- detoxification (as part of environmental toxin detoxification).
- obesity (metabolism stimulation in combination with a proper diet).
- major depression.
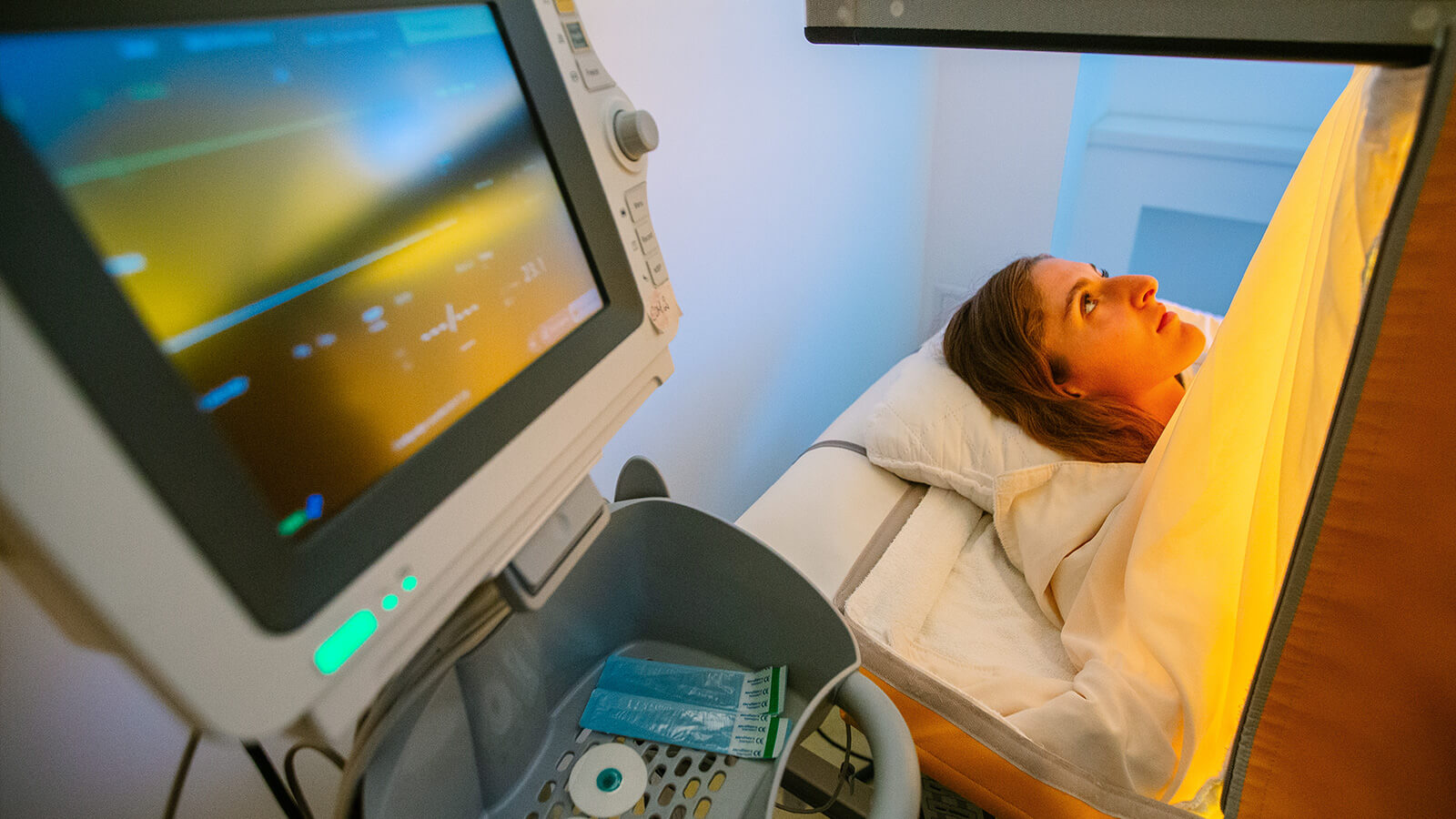
Procedure
The objective of systemic hyperthermia is to induce the beneficial effects that fever has on the body. Usually, during 3 hours, the temperature of 40-41ºC is induced, with the possibility of maintaining it at 38-40ºC for 4-8 hours.
By applying heat to the entire body, general hyperthermia treats systemic diseases, including cancer. As a result of abnormal vascularization, anaerobic metabolism and nutrient depletion, tumors have a higher thermal sensitivity than healthy tissues.
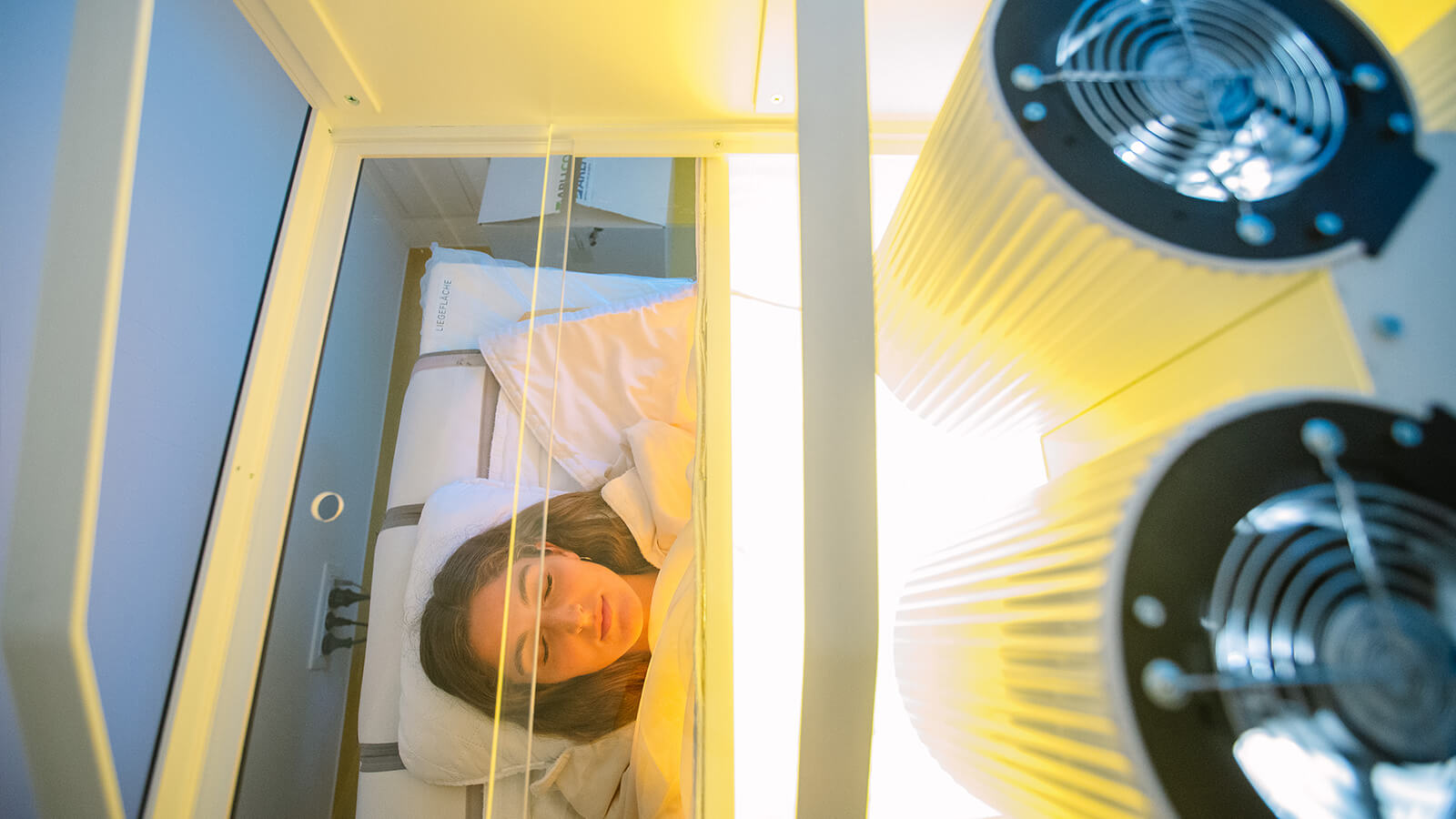

The patient is placed on a special bed, adjustable throughout the procedure, which may last for several hours, to ensure patient comfort throughout the session. Body temperature is increased by applying infrared radiation (IR-A). The patient makes minimal effort during this procedure, he relaxes in a pleasant and comfortable environment, during the several hours of temperature application. Throughout the entire procedure, body temperature, heart rate, oxygenation, blood pressure, EKG, respiratory rate are constantly monitored.
Total hyperthermia is administered in cycles of 4-6-8-10-12 sessions, consecutively carried out, one week apart from one another.
Recommendations
Treatment with hyperthermia may be applied in all stages of cancer. Countless clinical trials have studied the effects of combined hyperthermia treatment with radiotherapy or chemotherapy. These studies focused on treating several types of cancer, such as sarcomas, melanoma, head and neck cancer, brain, lung, esophageal, breast, urinary bladder, anal, liver, cervical, peritoneal cancer. Many of these studies showed a significant reduction in tumor volume, when hyperthermia was combined with other forms of treatment.
The main reasons for using general/systemic hyperthermia are the following:
- compared to healthy cells, cancer cells become more sensitive, even developing an intolerance to the effects of excessive heat,
- because the tumors do not have the capacity to adapt their blood circulation to the effects of the high temperatures, a decrease in their blood supply is registered,
- temperatures higher than 41ºC cause the appearance of acidosis in cancer cells, which decreases their viability and division capacity,
- high temperatures cause activation of the body's immune system, with increased interferon production. Renowned German doctor Rolf Issels has noticed that hyperthermia increases the concentration of heat shock proteins (HSPs) on the surface of cancer cells, thus making them prone to the attacks of the immune system,
- systemic hyperthermia may be successfully used for metastatic cancers.
The tumor mass, at its core, contains the cells that live in a state of hypoxia (with little oxygen). These cells have resistance to radiation treatment, but they are very sensitive to heat. Researchers believe that radiation therapy destroys normally oxygenated cells in the upper layers of the tumor, while hyperthermia acts on those within, greatly decreasing the overall resistance of the tumor to radiation or drug treatment.
Benefits
Clinical experience has shown that one of the greatest benefits of systemic hyperthermia is the increased efficiency of other forms of cancer treatment. Heating the cells at temperatures higher than the physiological ones makes them susceptible to radiation and chemotherapy treatment.
SPECIALIZED RESEARCH HAS SHOWN THAT
(GENERAL) SYSTEMIC HYPERTHERMIA CAN CAUSE:
- maturation of dendritic cells in the brain
- increased immune response (through the interaction of dendritic cells with CD8 T cells)
- prolonged activation of immune T cells
- activation of monocytes and macrophages
- release of tumor necrosis factor (TNFα)
- increased number of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells (NK)
- general stimulation of the body's immune response.
Moreover, under the influence of heat, tumor cells produce heat shock proteins (HSPs), specific to damaged cells in the body; their synthesis makes them susceptible to destruction by the immune system. Thus, hyperthermia stimulates the immune system to fight the tumor.
Currently, systemic hyperthermia is officially recognized as a classic, effective method of treating different forms of cancer.
Side effects and contraindications
Contraindications depend on the degree of elevation of the proposed temperature and are oriented according to the negative load exerted on the circulatory system and to the possibility of creating an unwanted activation of inflammation, as well as of destabilizing the hormonal and metabolic labile constellations:
- acute infections
- excessive dehydration with disturbances of the hydro-electrolyte balance in the body, anhidrosis
- heart failure (degree > 2)
- advanced atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction; heart rhythm disorders - (prior to the hyperthermic treatment, cardiac tests are required)
- extreme deficient cerebral circulation, brain tumors, possibly cerebral edema; as regards those disorders that have an intense rate of cancer metastasis, a medical examination is required prior to the hyperthermic therapy (the onset of convulsions during the oncological hyperthermic treatment indicates the existence of the brain cancer metastases that have not been diagnosed yet, which entails the immediate interruption of the therapeutic sessions)
- manifest insufficiency of internal organs such as lungs, liver, kidneys, bone marrow regarding obstructive neoplasms or destructive inflammatory processes
- diagnosed or suspected thrombosis, the anticoagulant drug Marcumar, peripheral arterial occlusive disease (in case of venous varicose veins, the patient's legs will be suspended and covered)
- for diseases with strong episodes, where treatments have unsatisfactory results, such as multiple sclerosis
- for episodes of primary-evolutionary chronic polyarthritis (rheumatoid arthritis)
- hormonal and metabolic crises such as hyperthyroidism and porphyria
- sugar diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus) and muscle hypertonia require a permanent discontinuation in advance
- oxygen saturation below 92%
- poor condition of general health of the patient in the advanced stages of a present disease (WHO 3rd or 4th degree)
- limit psychiatric situations
- pregnancy and breastfeeding
- a diagnosed lymphedema may be intensified after the hyperthermic treatment due to the vasodilation that occurs. In order to start a hyperthermic treatment, aware of the aforementioned risks, the patient must be informed about the seriousness of this decision. When affirmative, the hyperthermic process will be joined by adjuvant medications such as (enzyme therapy).
The main
adverse reactions are
- overloading of the circulatory system and of the regulation of the central body temperature in situations where it is forced to increase the temperature from the reference value of 37ºC to a much higher real value,
- thermal overloading of the main arteries affected by malperfusion (ischemia) or that have other special properties,
- unwanted effects of immune system stimulation and coronary perfusion.
How can you become a patient of our clinic?
Throughout the whole process, from your initial contact, through treatment and after you leave our clinic, our patient coordinators will guide you through the steps and support you with all their expertise, attention and kindness.
*
We are here to help you
Our patient coordinator will contact you soon
Phone: +40.771.518.946, e-mail: office@imuno-medica.ro




